Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
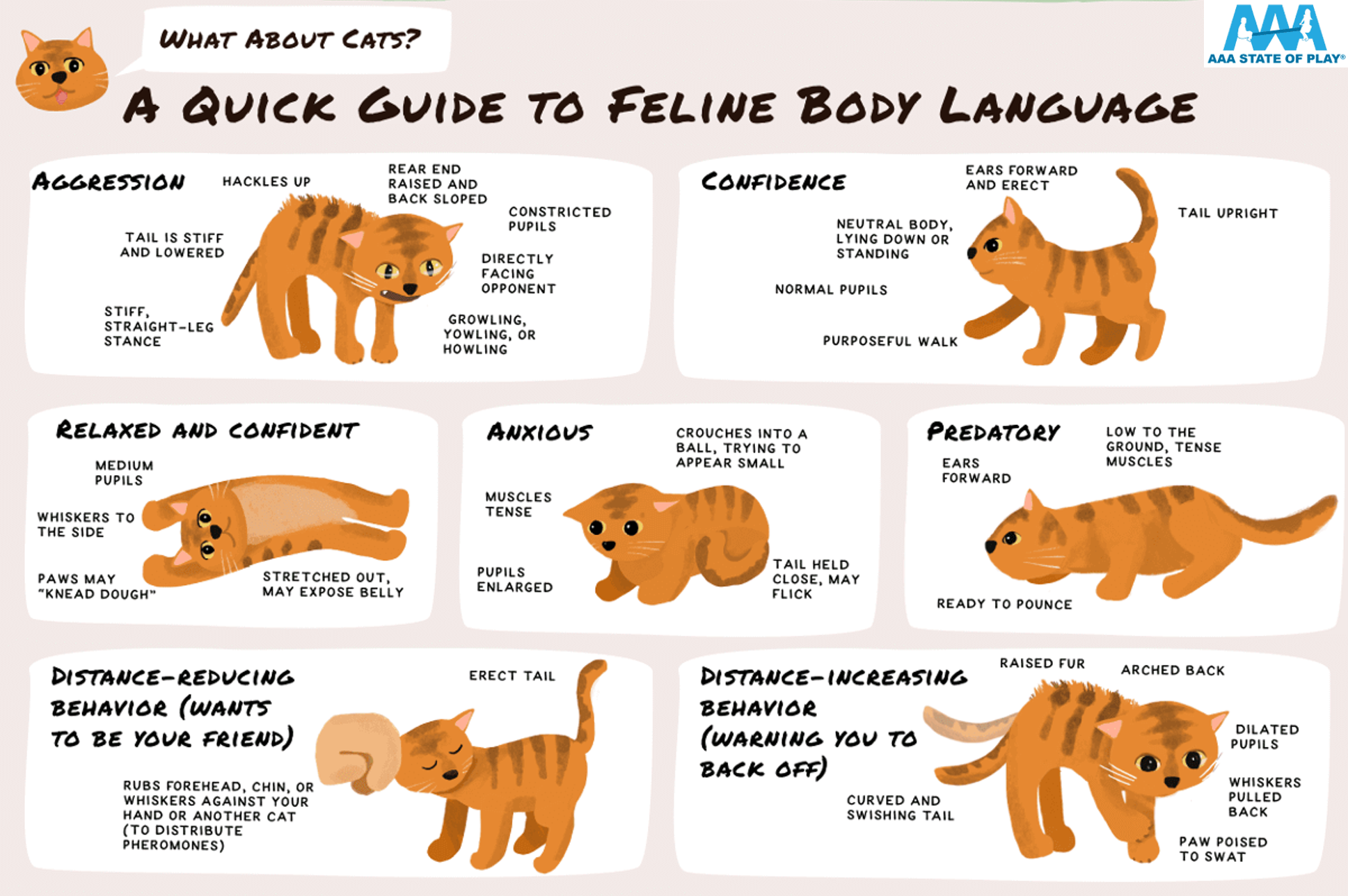
A Guide to the Body Language of Cats
Cats have long held the reputation of being enigmatic creatures, often leaving their human counterparts baffled by their behaviours. But fear not, fellow cat lovers, for in this comprehensive guide, I will be explaining the cat behaviour. By the end of this article, you'll be well on your way to understanding and strengthening the bond you share with your cat.
The Tale of the Tail
Cats are notorious for their tail-telling behaviours. In this section, we'll explore the various positions and movements of your cat's tail and what they reveal about their feelings.
Upright Tail: When your cat holds their tail high in the air, it usually signifies a content and confident cat. They are feeling happy and comfortable in their environment.
Puffed Tail: A puffed-up tail is a sign of extreme fear or agitation. This is often seen when a cat is confronted by something that terrifies them, like a larger animal or a loud noise.
Twitching Tail: A tail that's twitching or quivering can indicate excitement, irritation, or anticipation. Pay attention to other body language cues to determine the exact emotion.
Lashing Tail: A tail that's rapidly moving from side to side is a clear sign of an agitated or angry cat. This can be seen during play or when a cat is annoyed.
Lowered Tail: A tail that's held low to the ground but not tucked between the legs generally suggests that a cat is cautious or anxious. They might be unsure about their surroundings.
Tucked Tail: When a cat tucks their tail between their hind legs, it usually indicates fear or submission. They might be feeling threatened or uncomfortable.
Puffed Tail with Arched Back: This posture, often referred to as "bottlebrush tail," is a defensive one. A cat displaying this behaviour is trying to appear larger and scarier to intimidate a potential threat.
Curved Tail Tip: A tail with a slight curve at the tip indicates a friendly and approachable cat. This is often seen in cats greeting their owners.
Tail Held to One Side: If a cat holds their tail to one side, it can indicate curiosity or playfulness. They might be investigating something interesting.
Slow Wagging Tail: Unlike the fast lashing tail, a slow wagging tail can suggest that a cat is in a playful mood. It's often seen when they are focused on a toy or prey.
Ears and Whiskers - Windows to the Kitty Soul
Your cat's ears and whiskers are like antennas to their emotions. We'll delve into how the orientation of their ears can give you valuable insights into their mood. And yes, those twitching whiskers are not just for show; find out what they mean.
Cat Ears
Forward and Upright Ears: When a cat's ears are facing forward and upright, it generally means they are alert, attentive, and possibly interested in something. It's a sign of curiosity and readiness to explore.
Slightly Forward: Ears that are slightly forward but not fully upright suggest that a cat is in a friendly and sociable mood. They may be open to interaction or play.
Flat Backwards: When a cat's ears are pressed flat against their head, it usually indicates fear, aggression, or extreme discomfort. This is a defensive posture, and the cat may feel threatened.
Pinned Back: If a cat's ears are pinned tightly to their head, it often signifies aggression or irritation. Cats may pin their ears when they are annoyed or about to strike.
Slightly Sideways: Ears that are slightly tilted to the side can indicate uncertainty or wariness. It's a sign that the cat is not entirely comfortable with the situation.
Rotating Ears: Cats can rotate their ears to focus on specific sounds or movements. If your cat's ears are constantly moving or twitching, they are likely paying close attention to their environment.
Relaxed Ears: When a cat's ears are in a neutral position, neither forward nor backward, it generally means they are calm and content. This is often seen when a cat is at ease and relaxed.
One Ear Forward, One Ear Back: Sometimes, a cat may position one ear forward and one ear backward. This can indicate mixed emotions or that the cat is unsure about how to react to a particular situation.
Ears Back and Low: Ears that are low but not fully flattened against the head can indicate submission or fear. This may be seen when a cat is trying to avoid confrontation or appease a dominant cat or person.
Twitching or Flicking Ears: Rapid ear movements or twitching can signal annoyance or irritation. It's essential to pay attention to other body language cues to determine the cause of this irritation.
Cat Whiskers
Backward or Flattened Whiskers: Whiskers pressed flat against the face typically indicate fear, anxiety, or an attempt to avoid confrontation or discomfort.
Whiskers Pulled Back and to the Side: If a cat's whiskers are pulled backward and to the sides, it can be a sign of irritation, annoyance, or alertness. This is often seen when a cat is agitated or focused on something.
Twitching Whiskers: Rapid twitching or movement of the whiskers can indicate heightened excitement, anticipation, or irritation. This is commonly seen during play or when a cat is hunting.
Whisker Fatigue: Cats can experience "whisker fatigue" when their whiskers are overstimulated, causing discomfort. It's important to provide breaks and avoid touching their whiskers excessively.
Whisker Shedding: Some cats naturally shed their whiskers over time. This is a normal process, and new whiskers will grow in their place.
The Cat's Eyes - Mirrors of the Soul
Dilated Pupils: Enlarged or dilated pupils often indicate excitement, curiosity, or even aggression. Cats' pupils can change size rapidly in response to their emotional state and light levels.
Constricted Pupils: Narrowed or constricted pupils typically suggest that a cat is feeling stressed, anxious, or unwell. It can also be a sign of discomfort or pain.
Half-Closed Eyes: Cats often half-close their eyes when they are relaxed, content, or in a trusting and affectionate mood. This is often referred to as "cat kisses."
Rapid Blinking: Slow, deliberate blinking is a sign of affection and trust. When your cat blinks at you, try returning the slow blink to strengthen your bond.
Staring with Unblinking Eyes: Continuous, unbroken eye contact can be perceived as a challenge or threat in cat communication. It's best to avoid prolonged staring with unfamiliar cats.
Slow Blinking: Cats often slow blink at their owners as a sign of affection and trust. If your cat gives you a slow blink, try reciprocating it to convey your love.
Squinting: Squinting can indicate comfort and relaxation. It's common to see cats squint when they are enjoying a cozy nap in a sunny spot.
Wide-Eyed Stare: A wide-eyed, unblinking stare may be a sign of fear, aggression, or extreme alertness. In such cases, it's essential to approach the cat with caution and avoid provoking them.
Blinking One Eye: Blinking one eye at a time can be a playful or mischievous gesture. Cats may do this when they are in a playful mood.
The Vocal Mysteries
Cats may not meow in Morse code, but their vocalisations convey a lot if you know what to listen for. From purrs of pleasure to yowls of distress, we'll decipher the language of meows, chirps, and everything in between.
Standard Meow: This is often a general greeting or expression of mild interest. Your cat might be saying "hello" or trying to get your attention.
Prolonged Meow: A drawn-out meow may indicate a request or a demand. It's often associated with a desire for food, playtime, or access to a certain area, like going outside.
Short, High-Pitched Meow: Cats may use short, high-pitched meows when they are excited or in a playful mood. They may do this while chasing toys or anticipating play.
Loud, Insistent Meow: A loud and persistent meow is often a clear sign that your cat wants something urgently. This could be related to hunger, discomfort, or a specific need.
Chirping or Chattering Meow: Cats sometimes make chirping or chattering sounds when they are watching birds or other small prey animals. It's believed to be an expression of their hunting instincts and excitement.
Silent Meow: Some cats open their mouths as if to meow but produce no sound. This is often seen as a sign of affection and an attempt to communicate without making noise.
Hissing or Growling Meow: These meows are usually associated with aggression or fear. If your cat hisses or growls while meowing, it's best to give them space and avoid provoking them.
Whiny Meow: A whiny or complaining meow might indicate that your cat is unhappy about something, such as being held or placed in a carrier.
Trill Meow: A trill is a mix between a purr and a meow. Cats often use trills to greet their owners or show affection.
Repetitive Meowing: If your cat meows excessively and repetitively, it could be a sign of distress, anxiety, or illness. It's essential to monitor your cat's behavior and consult a veterinarian if this persists.
Body Posture and Gestures
In this section, we'll decode the subtle nuances of your cat's body postures. From the crouched hunter's stance to the playful belly-up flop, we'll uncover what your cat's gestures are saying about their comfort and intentions.
The Power of Purring
Purring is one of a cat's most intriguing behaviours. To understand your cat's purring better, pay attention to their body language, the situation, and their overall behaviour. A cat that's purring while being petted gently and has a relaxed body is likely content. On the other hand, a cat that's purring while hiding or exhibiting other signs of stress may be using purring as a coping mechanism.
Remember that each cat is unique, and their purring can vary depending on their personality and past experiences. Over time, you'll become more attuned to your cat's specific purring patterns and what they mean in different contexts, which will strengthen the bond between you and your feline friend.
Conclusion
Remember, your cat is constantly communicating with you; all you need to do is listen with an open heart and a curious mind. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey into the world of cat behaviours and strengthen the bond with your cat.
For more information, feel free to visit RSPCA and WebMD.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular Posts
The Science Behind Catnip: Why Do Cats Love It?
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps






Comments
Post a Comment